Explore the collection
Showing 89 items in the collection
89 items
Book
Lin Zhao: No Longer Forgotten
This book contains a number of articles in memory of Lin Zhao. It concerns the death of Lin Zhao as well as Lin Zhao's love, pursuits, and disillusionment. This book was published by Changjiang Literature and Art Publishing House in 2000.
Book
Liu Xiaobo Memorial Anthology
This book is a collection of essays in memory of the Nobel Peace Prize winner Liu Xiaobo. It was edited by Cai Chu following his death.
Book
Liushahe Essay
Liushahe is a famous Chinese writer and scholar, who entered Sichuan University in the fall of 1949, and was criticized and stigmatized nationwide during the 1957 Anti-Rightist Movement for his work *Grass and Trees* named by Mao Zedong himself, and then subjected to a variety of labor reforms (building roads during the day and sawing wood in the evening) for a cumulative total of 20 years. In 1979, he was transferred back to the Sichuan Provincial Literature Federation. Since 1985 he has been writing full-time, and has published a number of books, including *Essays on the Liusha River*. This book was published by Sichuan Literature and Art Publishing House in 1995. Many of the essays are related to his experiences when he was under labor reform. In November 2019, Liushahe passed away in Chengdu at the age of 88 due to illness.
Book
Living Monument in the Square: June 4 Bloodshed through the Eyes of a Hong Kong Woman Reporter
The author of this book was a reporter for "Sing Tao Daily" and was stationed in Beijing at the end of April 1989 to cover the democracy movement. The book is divided into six main parts: Square Facts records the course of the 1989 democracy movement, from the author's visit to Beijing in April to the early morning of June 4, when she and the masses were evacuated from Tiananmen Square. The second part concerns post-hijacking memories, which are some of the author's interviews from 1989. The third part concerns the interviews. The author had interviewed 7 student leaders and intellectuals that year. The leaders told her the reasons why they devoted themselves to the student movement. The fourth part is about the rest of the author's life, from June 4 to December 1990. The author has recorded some fragments of her speeches to the secondary school students in Hong Kong. Some of them are sentimental, some of them are confessional, and all of them are sincere and heartfelt. The fifth part is "Twenty Years of Wounds," which is a reminiscence written by the author on the 20th anniversary of June Fourth. The sixth part is about the grassroots of June 4. These grassroots actors have been pretty much forgotten. The author wanted to write a biography of the grassroots of June 4 in order to fill in gaps in history.
Book
Major Events, Tiananmen 1989
The author was a key member of the 1989 pro-democracy movement when he was teaching at the Chinese University of Political Science and Law. After the June 4 massacre, he went into exile. Currently, he has settled in Taiwan, where he teaches a course on the truth of the June Fourth Incident at Soochow University and National Chung Cheng University. Wu Renhua has published several books related to the June Fourth Incident. With a master's degree in Classical Literature from Peking University, he has written a book on June 4 that emphasizes the reliability of the sources of information. This book records the major events that happened every day during the June 4 period (April 15th to June 9th).
Film and Video
Memory of Lin Zhao
Independent director Tiger Temple began shooting this film in 2010 and completed it in 2012, with subsequent revisions. The film features interviews with Lin Zhao's former lover Gan Cui as well as interviews with several independent scholars such as Qian Liqun and Cui Weiping. It is a powerful addition to Lin Zhao's memory. This film was selected as one of the top 20 finalists in the 2012 Sunshine Chinese Documentary Awards.
Book
Monologue of a Doomsday Survivor: About Me and June 4
购书链接:https://www.kobo.com/hk/zh/ebook/ZoerWPfG8TiqoXIYwvW2iw。
Article
My Father Xu Liangying
Xu Liangying is a well-known Chinese physicist, thinker and social activist. He has translated “The Collected Works of Albert Einstein”, published by The Commercial Press (three volumes, 1979). He was branded as a rightist in his youth, but in his later years he pursued constitutional democracy and became an outspoken public intellectual. This is a memoir written by his son Xu Ping after his passing in 2013.
Article
My Life: China's Direction
When the Cultural Revolution broke out, Yang Xiaokai was a senior high school student at No. 1 Middle School in Changsha. On January 12, 1968, he published an article entitled "Where is China Going?" which systematically put forward the ideas of the "ultra-leftist" Red Guards, criticized the privileged bureaucratic class in China, and advocated for the establishment of a Chinese People's Commune based on the principles of the Paris Commune. Yang Xiaokai recalled that his parents were beaten because they sympathized with Liu Shaoqi's and Peng Dehuai's views, and that he was discriminated against at school and could not join the Red Guards. As a result, he joined the rebel faction to oppose the theory of descent. Yang Xiaokai was later sentenced to 10 years' imprisonment for this article. Yang Xiaokai died in 2004. This article is a retrospective of his life.
Book
New Biographies of the 1957 Rightists
According to official CCP statistics, some 550,000 people were directly labeled as rightists and persecuted during the Anti-Rightist campaign. These people, as well as others implicated in the campaign, are mostly unknown, except for a very few. The author, Shen Yuan, who was also labeled as a rightist when he was a university student in 1958, devoted himself to collecting and researching historical data on the anti-rightist campaign. He has compiled a book entitled Biographies of the 1957 Rightists, which attempts to present the truth about the Anti-Rightist campaign and its victims. The book is divided into four volumes of about 1.2 million words, containing the stories of about 600 rightists and about 240 historical photographs. 2016 marked the 60th anniversary of the Anti-Rightist campaign, and Shen Yuan used the original book as the basis for his New Biographies of the 1957 Rightists, expanding the number of people included to 1,588. Sha Yexin and Wu Yisan were both involved in the compilation of this book.
Film and Video
New Citizens’ Trial
In late January 2014, on the eve of the Lunar New Year, Xu Zhiyong, Zhao Changqing, Ding Jiaxi and other advocates of the New Citizens’ Movement were charged with "gathering a crowd to disrupt order in a public place." The case was heard for the first time in courts at different levels in Beijing. This film intersperses on-site records with interviews with defense lawyer Zhang Qingfang, scholar Guo Yuhua, entrepreneur Wang Ying, and others to present citizens' understanding of the New Citizens' Movement.
This series of films are in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Book
Newly Discovered Mao, The: Volume I
Author Wang Ruoshui spent his early years studying philosophy at Peking University. He served as deputy editor-in-chief of the Communist Party newspaper “People's Daily” and was able to participate in high-level ideological discussions, gaining a deep understanding of Mao Zedong as a person and of his thought. He was one of the rare intellectuals within the CCP system who had an independent personality as well as the ability to think for himself. After his death from cancer, his wife, Feng Yuan, helped put together this posthumous book. Published by Ming Pao Press in 2002, it has been described as "the first and most comprehensive and in-depth discussion of Mao Zedong and his thought."
Book
Newly Discovered Mao, The: Volume II
Author Wang Ruoshui spent his early years studying philosophy at Peking University. He served as deputy editor-in-chief of the Communist Party newspaper "People's Daily" and was able to participate in high-level ideological discussions, gaining a deep understanding of Mao Zedong as a person and his thought. He was one of the rare intellectuals within the CCP system who had an independent personality as well as the ability to think for himself. After his death from cancer, his wife, Feng Yuan, put together this posthumous book. Published by Ming Pao Press in 2002, it has been described as "the first and most comprehensive and in-depth discussion of Mao Zedong and his thought.
Article
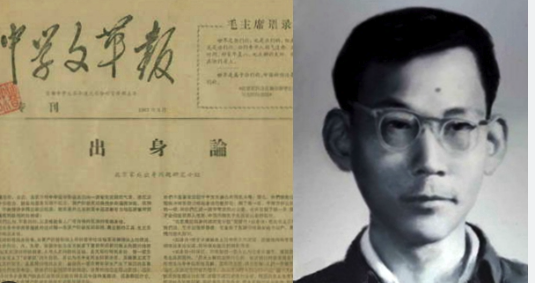
On Family Background
Yu Luoke (May 1, 1942 - March 5, 1970): Worker, freelance writer, and public intellectual.
Yu was born into an educated family in northeastern China, which for a period of time was under Japanese occupation. His father studied on a state scholarship in Waseda University in Tokyo, while his mother came from a wealthy family in Beijing and studied business at Tokyo Girls High School. When the two returned to China, they went into business, married, and had three children.
When the CCP took power, the family was declared part of the “bourgeois class” and like other “black elements”--classes of people who the party declared to be enemies–was persecuted. The father was arrested in 1952 on charges of tax evasion and released. In 1957, Yu Luoke’s parents were declared Rightists and sent to labor camps. In 1959, Yu graduated from high school with highest honors but as the offspring of an undesirable class was not permitted to attend university. In 1961, he was allowed to work on a farm in a Beijing suburb, where he realized that class identity was also important in rural China–landlords and their children were even beaten to death. In 1964 he returned to the city and apprenticed at a machinery factory. Yu realized that he was part of an untouchable caste in Maoist China and would be condemned forever, no matter what he believed or how hard he worked.
These experiences were the genesis of Yu’s essay, which became one of the most famous texts of the Mao era. Yu wrote it at the start of the Cultural Revolution. The ten-thousand character essay is called chushenglun, or “On Family Background” (sometimes translated as “On Class Origins"). In it, he warned that the “five black categories'' were becoming a permanent underclass, while China’s rulers were from the hongwulei, or “five red categories:” poor and lower-middle peasants, workers, revolutionary soldiers, revolutionary officials, and revolutionary martyrs, including their family members, children, and grandchildren. He warned of a new ruling class based on bloodlines.
The essay was published in a journal that Yu and his brother Yu Luowen called the "Journal of Secondary School Cultural Revolution." In January 1967, about thirty thousand copies were printed, and the young men began distributing them around the capital, selling them for two cents a copy. They sold out in a few hours. In February, they printed another eighty thousand copies.
Soon, hundreds of letters each day arrived at Yu Luoke’s local post office—so many that he had to go collect them in person. The missives detailed how the Communists’ policies had caused them to suffer. People traveled from across China to visit them at their home, excited that someone finally had uncovered how the Chinese Communist Party ruled. The editorial board was expanded to twenty people, and the group sponsored debates and seminars.
The Journal was closed down in April 1967. Yu Luoke began to write on economic inequality. In January 1968, he was arrested. Two years later, on 5 March 1970, Yu was executed by firing squad at Beijing Workers Stadium.
Article
Operation Yellow Bird
After the bloody suppression of the June 4 Democracy Movement, the Chinese Communist Party went on a massive manhunt for the key figures of the movement. Some Hong Kong people organized a secret channel to help pro-democracy activists escape from the Mainland, codenamed "Operation Yellow Bird." The author of this book, Jiang Xun, is a veteran of the media and describes in detail how the "Yellow Bird Operation" took place.
Film and Video
People’s Representative Yao Lifa
Yao Lifa, a teacher from Hubei, was an independent candidate for the 2003 General Election of Deputies to the National People’s Congress. This documentary records the process in which Yao publicized and educated the public on election laws, and his experience with the grassroot electoral campaign. This documentary also reflects the budding grassroot awareness of civil rights in China through voices from the media and ordinary people.
This film is in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Book
Personal experiences of political movements
This book is a collection of many authors, most of whom were former senior officials of the Communist Party of China, such as Li Rui, Xiao Ke and others. Through the author's recollections, we can learn about the political movements of the Mao Zedong era, including the Cultural Revolution, the Anti-Rightist Movement, etc., as well as the details of many unjust cases, such as the Hu Feng case, which is quite convincing. This book was published by the Central Compilation and Translation Bureau Press in mainland China in 1998.
Book
Remembering Tiananmen Square
The author was a Hong Kong-based observer for the international human rights organization Human Rights Watch. Remembering Tiananmen is a long article first published in The Nationmagazine in November 1990. It was written after witnessing the crackdown around the square during the night of June 3 until 4 a.m. the next morning.
Book
Rethinking China's Democracy Movement
Author Hu Ping was involved in the Xidan Democracy Wall movement in the late 1970s and now lives in the United States.
He has successively chaired the pro-democracy publications <i>China Spring</i> and <i>Beijing Spring</i>. This book, published in 1992, analyzes the reasons for the failure of the June Fourth Movement and summarizes the lessons learned. The last two chapters suggest how to continue the pro-democracy movement in the future.
Book
Revisiting 1957
<i>Revisiting 1957</i> is not just about the history of the Anti-Rightist Campaign but is also a theoretical reflection on that history. Written by Wei Zidan (the penname for Wei Liyan), the book has three sections: upper, in which the author discusses philosophical problems of the campaign; middle, in which he discusses the origins of the campaign; and lower, which contains his thoughts on lessons for the future. In Wei's view, the people who were declared rightists stood up for freedom of speech. The campaign, therefore, was an assault on freedom of expression and resulted in a human rights catastrophe for China. The book also has an eleven-part appendix with reflections on miscellaneous events.
Wei Zidan was born in Henan Province in 1933 and was a teacher in the Anyang Middle School. He himself was labeled a rightist and brings a unique insider's account of the movement but unlike some personal accounts of suffering, Wei also brings a more analytical approach to the issue.
After moving to the United States in his later years, he collected information and found the freedom to complete this book. Published in Hong Kong in 2013 by the May 7 Society Press.