Explore the collection
Showing 90 items in the collection
90 items
Book
Liushahe Essay
Liushahe is a famous Chinese writer and scholar, who entered Sichuan University in the fall of 1949, and was criticized and stigmatized nationwide during the 1957 Anti-Rightist Movement for his work *Grass and Trees* named by Mao Zedong himself, and then subjected to a variety of labor reforms (building roads during the day and sawing wood in the evening) for a cumulative total of 20 years. In 1979, he was transferred back to the Sichuan Provincial Literature Federation. Since 1985 he has been writing full-time, and has published a number of books, including *Essays on the Liusha River*. This book was published by Sichuan Literature and Art Publishing House in 1995. Many of the essays are related to his experiences when he was under labor reform. In November 2019, Liushahe passed away in Chengdu at the age of 88 due to illness.
Book
Lushan meeting factual record
This book is a historical record of the 1959 Lushan Conference written by Li Rui. Based on the author's personal experience and the literature of the relevant departments of the Communist Party of China, the author has recorded the important points and events before and after the meeting. The first edition of this book was published in April 1989 by the Spring and Autumn Publishing House and Hunan Education Publishing House in mainland China; the updated edition was published in June 1994 by Henan People's Publishing House.
Book
Mao in Power (1949-1976)
The author of this book, Shan Shaojie, is a scholar from mainland China. For several years, he wrote this book from an independent position. Former political secretary of Mao Zedong, Li Rui, and Princeton University professor, Yu Yingshi, wrote the foreword for this book. In addition to a systematic account of the Maoist era, Shan Shaojie's book "Mao in Power" emphasizes that almost all members of the Communist Party's highest decision-making echelons, with the exception of Mao Zedong, made efforts, in varying degrees and successively, to stop Mao's insanity. Moreover, they took turns to resist and ultimately to leave Mao alone, but did not really stop Mao's madness. This book was published by Linking Publishing in 2001 and has been reprinted several times.
Book
Mao Zedong and the Cultural Revolution: an interpretation of political psychology and cultural genes
This book systematically explores the mental world of Mao Zedong, and his followers (including Lin Biao, Jiang Qing, Zhou Enlai, Kang Sheng, and Zhang Chunqiao). According to the author, it involves lust, political fantasies, and other pathologies. The book analyzes how these subconscious thoughts underlay the history of the Cultural Revolution.
Book
Mao: The Unknown Story
This book presents the dramatic life of Mao Zedong, revealing a wealth of unheard-of facts: why Mao joined the Communist Party, how he came to sit at the top of the Chinese Communist Party, and how he seized China step by step. Writers Jung Chang and her husband Jon Halliday took ten years to complete this book, interviewing hundreds of Mao's relatives and friends, Chinese and foreign informants and witnesses who worked and interacted with Mao as well as dignitaries from various countries.
Purchase link:https://www.amazon.com/Mao-Story-Jung-Chang/dp/0679746323.
Book
Memo of the Educated Youth: Production and Construction Corps of the "Down to the Countryside" Movement
During the Cultural Revolution, 14.03 million urban junior and senior high school students said goodbye to their parents and families and left the cities to receive "re-education" in the "wide world." 10.48 million young intellectuals who had been sent to the army or returned to their hometowns were resettled in rural communities and squads. 1.26 million were placed in the newly-formed youth collectives and teams, while another 2.29 million were accepted by state-run farms and production and construction corps. The production and construction corps became the most concentrated place for intellectual youths, and had an undeniably important position in the whole movement of educated youths going to the countryside. This book describes the rise and fall of the production and construction corps and the fate of the educated youths who went to the countryside during the Cultural Revolution.
Book
Memoirs of Sima Lu: A Witness to the History of the Chinese Communist Party, The
Sima Lu (1919-2021) was an expert on the history of the Chinese Communist Party. He joined the Chinese Communist Party in 1937, then was politically persecuted in Yan'an, left it, and was expelled from the Party in 1941. In 1952, Sima Lu published “Eighteen Years of Struggle” in Hong Kong, writing about his tortuous journey from defecting to the Communist Party to his awakening and eventual choice of freedom. It became a sensation. He has made in-depth special studies on several leading figures of the CCP, such as Qu Qubai and Zhang Guotao. His memoir, “Witness to the History of the CCP”, is divided into three chapters according to its contents: the first is about his personal experience, the second about the first generation of CCP figures, and the third is devoted to the struggle between Mao Zedong and Zhou Enlai.
Film and Video
Memory of Lin Zhao
Independent director Tiger Temple began shooting this film in 2010 and completed it in 2012, with subsequent revisions. The film features interviews with Lin Zhao's former lover Gan Cui as well as interviews with several independent scholars such as Qian Liqun and Cui Weiping. It is a powerful addition to Lin Zhao's memory. This film was selected as one of the top 20 finalists in the 2012 Sunshine Chinese Documentary Awards.
Article
My Father Xu Liangying
Xu Liangying is a well-known Chinese physicist, thinker and social activist. He has translated “The Collected Works of Albert Einstein”, published by The Commercial Press (three volumes, 1979). He was branded as a rightist in his youth, but in his later years he pursued constitutional democracy and became an outspoken public intellectual. This is a memoir written by his son Xu Ping after his passing in 2013.
Article
My Life: China's Direction
When the Cultural Revolution broke out, Yang Xiaokai was a senior high school student at No. 1 Middle School in Changsha. On January 12, 1968, he published an article entitled "Where is China Going?" which systematically put forward the ideas of the "ultra-leftist" Red Guards, criticized the privileged bureaucratic class in China, and advocated for the establishment of a Chinese People's Commune based on the principles of the Paris Commune. Yang Xiaokai recalled that his parents were beaten because they sympathized with Liu Shaoqi's and Peng Dehuai's views, and that he was discriminated against at school and could not join the Red Guards. As a result, he joined the rebel faction to oppose the theory of descent. Yang Xiaokai was later sentenced to 10 years' imprisonment for this article. Yang Xiaokai died in 2004. This article is a retrospective of his life.
Book
My Thirty Years of Re-education through Labor
The author of this book, a graduate of Yanjing University and a former employee of the Ministry of Finance of the Kuomintang government, was retained by the Chinese Communist Party after 1949. In 1951, he was sentenced to 12 years' imprisonment on the trumped-up charge of "counter-revolution" by the CCP for "suppressing the counter-revolution". During his imprisonment, he suffered horrors and hardships. Upon completion of his sentence, he was forced to "voluntarily stay in the field for employment," and in 1982 he was rehabilitated. After the June 4 massacre in 1989, he took up the pen at the age of 76 to describe this counter-revolutionary campaign. The book records many historical facts of the incarcerated labor reform and political campaigns in a down-to-earth and objective manner, providing details and supporting evidence for the study of this period of history.
The book can be purchased at https://www.amazon.com/%E9%95%87%E5%8F%8D%E6%B2%89%E5%86%A4-%E6%88%91%E7%9A%84%E5%8A%B3%E6%94%B9%E4%B8%89%E5%8D%81%E5%B9%B4-Chinese-%E4%B8%95%E5%BF%A0-%E7%8E%8B/dp/1685600263?.
Book
New Biographies of the 1957 Rightists
According to official CCP statistics, some 550,000 people were directly labeled as rightists and persecuted during the Anti-Rightist campaign. These people, as well as others implicated in the campaign, are mostly unknown, except for a very few. The author, Shen Yuan, who was also labeled as a rightist when he was a university student in 1958, devoted himself to collecting and researching historical data on the anti-rightist campaign. He has compiled a book entitled Biographies of the 1957 Rightists, which attempts to present the truth about the Anti-Rightist campaign and its victims. The book is divided into four volumes of about 1.2 million words, containing the stories of about 600 rightists and about 240 historical photographs. 2016 marked the 60th anniversary of the Anti-Rightist campaign, and Shen Yuan used the original book as the basis for his New Biographies of the 1957 Rightists, expanding the number of people included to 1,588. Sha Yexin and Wu Yisan were both involved in the compilation of this book.
Book
Newly Discovered Mao, The: Volume I
Author Wang Ruoshui spent his early years studying philosophy at Peking University. He served as deputy editor-in-chief of the Communist Party newspaper “People's Daily” and was able to participate in high-level ideological discussions, gaining a deep understanding of Mao Zedong as a person and of his thought. He was one of the rare intellectuals within the CCP system who had an independent personality as well as the ability to think for himself. After his death from cancer, his wife, Feng Yuan, helped put together this posthumous book. Published by Ming Pao Press in 2002, it has been described as "the first and most comprehensive and in-depth discussion of Mao Zedong and his thought."
Book
Newly Discovered Mao, The: Volume II
Author Wang Ruoshui spent his early years studying philosophy at Peking University. He served as deputy editor-in-chief of the Communist Party newspaper "People's Daily" and was able to participate in high-level ideological discussions, gaining a deep understanding of Mao Zedong as a person and his thought. He was one of the rare intellectuals within the CCP system who had an independent personality as well as the ability to think for himself. After his death from cancer, his wife, Feng Yuan, put together this posthumous book. Published by Ming Pao Press in 2002, it has been described as "the first and most comprehensive and in-depth discussion of Mao Zedong and his thought.
Article
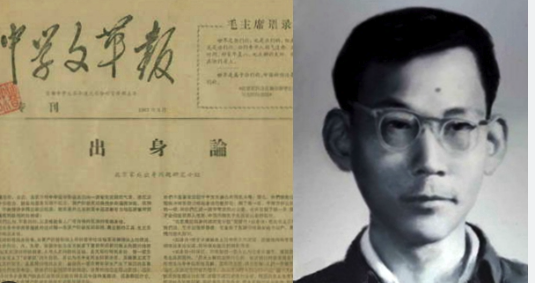
On Family Background
Yu Luoke (May 1, 1942 - March 5, 1970): Worker, freelance writer, and public intellectual.
Yu was born into an educated family in northeastern China, which for a period of time was under Japanese occupation. His father studied on a state scholarship in Waseda University in Tokyo, while his mother came from a wealthy family in Beijing and studied business at Tokyo Girls High School. When the two returned to China, they went into business, married, and had three children.
When the CCP took power, the family was declared part of the “bourgeois class” and like other “black elements”--classes of people who the party declared to be enemies–was persecuted. The father was arrested in 1952 on charges of tax evasion and released. In 1957, Yu Luoke’s parents were declared Rightists and sent to labor camps. In 1959, Yu graduated from high school with highest honors but as the offspring of an undesirable class was not permitted to attend university. In 1961, he was allowed to work on a farm in a Beijing suburb, where he realized that class identity was also important in rural China–landlords and their children were even beaten to death. In 1964 he returned to the city and apprenticed at a machinery factory. Yu realized that he was part of an untouchable caste in Maoist China and would be condemned forever, no matter what he believed or how hard he worked.
These experiences were the genesis of Yu’s essay, which became one of the most famous texts of the Mao era. Yu wrote it at the start of the Cultural Revolution. The ten-thousand character essay is called chushenglun, or “On Family Background” (sometimes translated as “On Class Origins"). In it, he warned that the “five black categories'' were becoming a permanent underclass, while China’s rulers were from the hongwulei, or “five red categories:” poor and lower-middle peasants, workers, revolutionary soldiers, revolutionary officials, and revolutionary martyrs, including their family members, children, and grandchildren. He warned of a new ruling class based on bloodlines.
The essay was published in a journal that Yu and his brother Yu Luowen called the "Journal of Secondary School Cultural Revolution." In January 1967, about thirty thousand copies were printed, and the young men began distributing them around the capital, selling them for two cents a copy. They sold out in a few hours. In February, they printed another eighty thousand copies.
Soon, hundreds of letters each day arrived at Yu Luoke’s local post office—so many that he had to go collect them in person. The missives detailed how the Communists’ policies had caused them to suffer. People traveled from across China to visit them at their home, excited that someone finally had uncovered how the Chinese Communist Party ruled. The editorial board was expanded to twenty people, and the group sponsored debates and seminars.
The Journal was closed down in April 1967. Yu Luoke began to write on economic inequality. In January 1968, he was arrested. Two years later, on 5 March 1970, Yu was executed by firing squad at Beijing Workers Stadium.
Book
Personal experiences of political movements
This book is a collection of many authors, most of whom were former senior officials of the Communist Party of China, such as Li Rui, Xiao Ke and others. Through the author's recollections, we can learn about the political movements of the Mao Zedong era, including the Cultural Revolution, the Anti-Rightist Movement, etc., as well as the details of many unjust cases, such as the Hu Feng case, which is quite convincing. This book was published by the Central Compilation and Translation Bureau Press in mainland China in 1998.
Book
Political Struggles in China's Reform Era
The author of this book, Yang Jisheng, is a veteran journalist with 35 years of experience in journalism at Xinhua News Agency, China's official news organization. He knows a great deal about the ups and downs of Chinese politics after the end of the Cultural Revolution as well as the intricate power struggles at the top and has a lot of first-hand information. He personally interviewed Zhao Ziyang, Zhu Houze, Li Rui, Ren Zhongyi, An Zhiwen, Tian Jiyun, and other important people. “Political Struggles in China's Reform Era”, first published in Hong Kong in November 2004, was the subject of a series of crackdowns by the authorities against Yang Jisheng. It was republished in 2010 by Hong Kong's Cosmo Books.
Article
Poppies under the Red Sun: The Opium Trade and the Yan'an Model
In the 1990s, history scholar Chen Yongfa made a fundamental study of the opium economy two decades before the founding of the CCP and completed a monograph, "Poppies under the Red Sun: The Opium Trade and the Yan'an Model". Since then, more and more research articles have been written on the subject, and new information has appeared. Subsequently, the phenomenon of the opium economy of the CCP's Yan'an regime has also became an important field of study.
Book
Prisoner of the State: The Secret Journal of Premier Zhao Ziyang
“The Course of Reform”, a memoir by Zhao Ziyang, former General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China, was published on May 29, 2009 by New Century Press in Hong Kong. Its English translation, “Prisoner of the State: The Secret Journal of Premier Zhao Ziyang” was published on May 13 before that. According to the book's preface, in 1992, Du Guanzheng, an old subordinate of Zhao Ziyang and former director of the State Press and Publication Administration, together with Xiao Hongda, another former high-ranking CCP official, persuaded Zhao Ziyang, who was under house arrest, to organize his experiences into a book.
Purchase link: https://www.kobo.com/hk/zh/ebook/ZoerWPfG8TiqoXIYwvW2iw.
Film and Video
Ram
The documentary "Ram" was filmed by independent director Tiger Temple in 2016 and is available here in a revised version by the author in 2021. The film documents a real-life incident that took place in Xi'an during the "1983 crackdown". The encounter of the artist Gong Yang (real name Li Xiaoming), the main character of the documentary, is quite representative. It reflects the cruelty and absurdity of the "1983 Crackdown" political campaign launched under the direction of Deng Xiaoping.