Explore the collection
Showing 19 items in the collection
19 items
Film and Video
Care and Love
This film records the story of Liu Xianhong, a woman from rural Xingtai, Hebei, who contracted AIDS through a blood transfusion in the hospital and decided to publicly disclose her identity and sue the hospital. After fighting in the courts, she finally received compensation. This documentary demonstrates the surging awareness of civil rights in rural China at the grassroot level through depicting the experiences of several families and the concerted efforts of patients to form “care” groups to collectively defend their civil rights. Due to public awareness, media intervention, and legal aid, the government also introduced new policies to improve the situations of patients and their families.
This film is in Chinese with both English and Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Chronicle of Western Liaoning, A
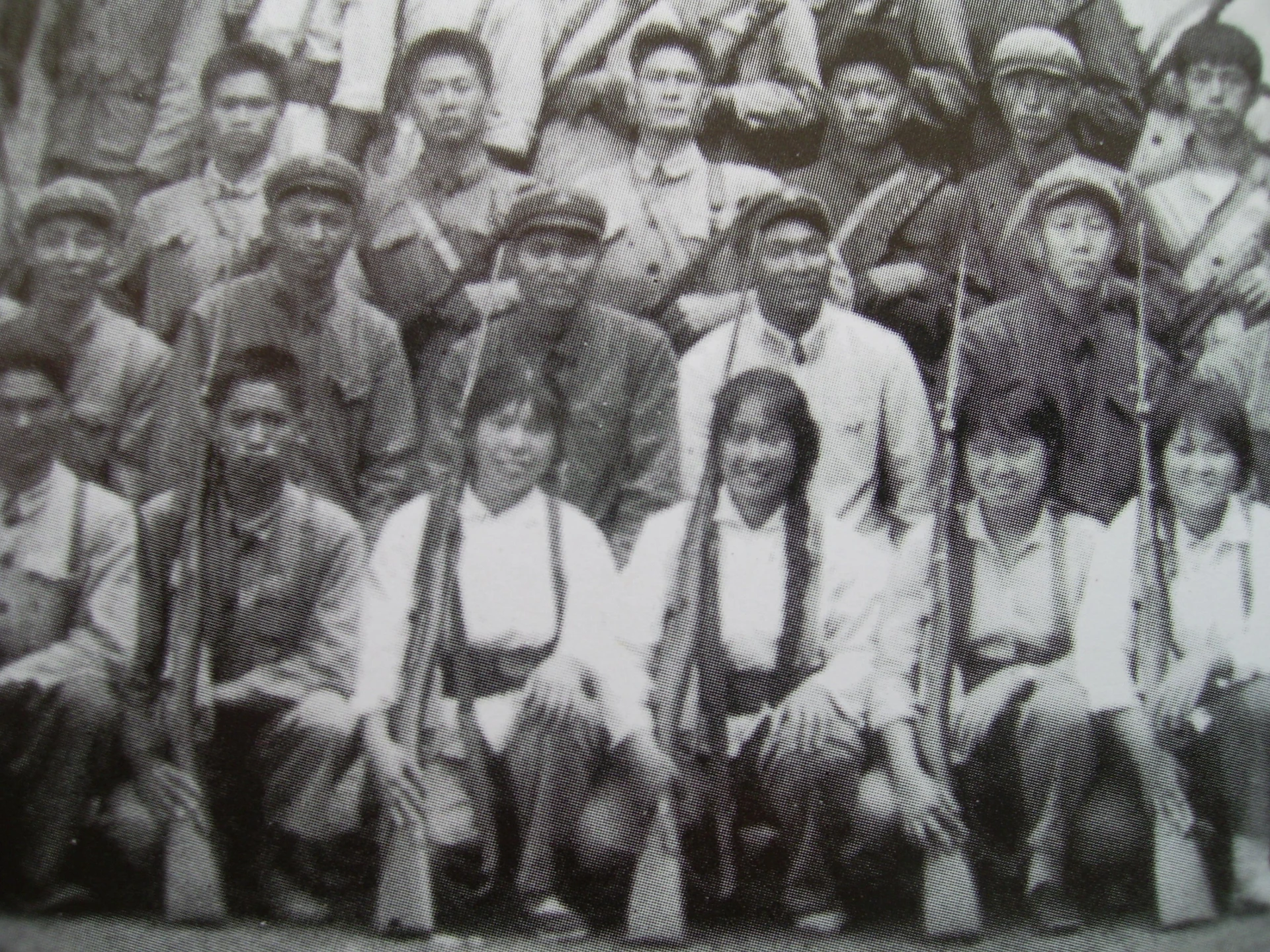
In 1959, in the desolate Lingyuan area in the western part of Liaoning Province, a group of intellectual rightists from the Shenyang University arrived. There, they were to labor and be reformed alongside criminal prisoners in the prison, while digging mines to build railroads. How did the Communist Party reform the intellectuals? What kind of encounters did these rightist intellectuals go through? Hu Jie's camera restores this history.
Film and Video
East Wind State Farm
In 1957, two hundred teachers, students, and cadres from Kunming, Yunnan were among the hundreds of thousands of Chinese people labeled as “Rightists” for criticizing the Chinese Communist Party. They were sent to the East Wind State Farm, located in Mi-le County in Yunnan, for 21 years of “thought reform” in the countryside. These inmates witnessed the policies of the Great Leap Forward first-hand: they took part in deforestation, agricultural, and industrial projects in the countryside, which precipitated the Great Famine. Later, during the Cultural Revolution, their camp was visited by large groups of youths “sent down” from the cities, who worked on the farm with the “Rightists.” In 1978, these “Rightists” were finally rehabilitated and allowed to leave.
This documentary examines the policies and campaigns of the Maoist era through the eyes of those who were persecuted and exiled. Director Hu Jie pieces together this long and complex story through collecting dozens of extensive interviews with inmates as well as staff who served through decades of the camp’s existence. These people’s vivid memories and personal accounts shed light on the harrowing lifestyle of not only the two hundred “Rightists” of East Wind State Farm, but also the scores of dissidents and youths who experienced the Great Leap Forward and the Cultural Revolution.
Film and Video
Garden of Paradise
The year 2003 was known as the birth of the Weiquan—the rights defense–movement, which was marked by the Sun Zhigang incident in Guangzhou. At the same time, a campaign began to get justice for Huang Jing, a teacher from Hunan who was sexually assaulted and killed by her boyfriend. The campaign involved the victim’s family, netizens, feminist scholars and activists, and lasted for several years. This documentary records the process of Huang Jing’s case from filing to post-judgement, and analyzes the broader issue of sexual violence against women in China.
The films in this series are in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Let the Sunshine Reach the Earth
Wang Lihong is a Beijing netizen, civilian journalist, and public service volunteer. Wang was accused of “picking quarrels and provoking trouble” for supporting three netizens in Fujian. On August 12, 2011, the case was heard for the first time in the Wenyuhe Court of the People's Court of Chaoyang District, Beijing. This film includes interviews with Wang Lihong's relatives, friends, defense lawyers and netizens, and records the historical scene of onlookers in the courts.
Ai Xiaoming’s film “Postcard,” also released in 2011, elaborates Wang Lihong’s activism in broader strokes, while “Let the Sunshine Reach the Earth” focuses on the process of her trial.
This film is in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Matchmaker, The
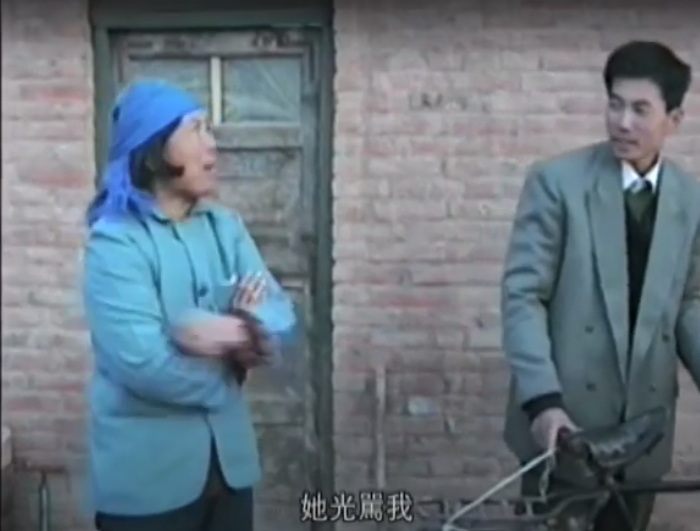
The tradition of matchmaking is still prevalent in northern rural areas today. This film records the story of Yang Xiuting, a matchmaker living in Guan County, Shandong Province. It describes how, due to economic reforms, rural people went to cities to find work. Subsequently, young people began to choose their own spouses. Thus, the ancient profession of matchmaker not only faces challenges, but also encounters new problems.
Film and Video
My Mother Wang Peiying
On January 27, 1970, Wang Peiying, a cleaner at a kindergarten in Beijing, was sentenced for counter-revolutionary crimes at a 100,000-person public trial held at the Workers' Stadium in Beijing. She was then taken to the execution ground along with a dozen other political prisoners to be executed by firing squad. Wang Peiying was strangled to death in the torture wagon because she preferred to die rather than give in and shout slogans. Forty years later, her daughter, Kexin, began to search for her mother's story. Through her mother's coworkers, friends in distress, and the task force, she gradually discovers her mother's experience as an active counterrevolutionary. In order to protect her conscience, Wang Peiying chose to stand up for her dignity and freedom to tell the truth, and willingly endured brutal torture. The documentary reflects the brutality of the Cultural Revolution and the destruction of humanity.
Film and Video
New Citizens’ Trial
In late January 2014, on the eve of the Lunar New Year, Xu Zhiyong, Zhao Changqing, Ding Jiaxi and other advocates of the New Citizens’ Movement were charged with "gathering a crowd to disrupt order in a public place." The case was heard for the first time in courts at different levels in Beijing. This film intersperses on-site records with interviews with defense lawyer Zhang Qingfang, scholar Guo Yuhua, entrepreneur Wang Ying, and others to present citizens' understanding of the New Citizens' Movement.
This series of films are in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Our Children
This documentary records the stories of the 2008 Sichuan earthquake. The narrators mainly consist of the parents of students who fell victim to the earthquake, and the film is interspersed with comments from media workers, independent scholars, internet authors, geologists, and environmental protection and legal workers. They expressed their views on the Sichuan earthquake from different perspectives.
This film is in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Postcard
After retiring from her job as a cadre, Wang Lihong fulfilled what she saw as her civic responsibility to become more active in women’s rights in China, especially the protection of their legal rights. In 2009-2010, she became involved in the “Fujian Netizen Case,” which resulted in the arrest of three human rights activists, who all sought to investigate the death of a 25-year-old women believed to have been murdered in a gang rape by men associated with the local police. Wang Lihong wrote letters to the General Secretary of the Fujian Provincial Committee of the Communist Party of China every day for nine consecutive days, calling on the authorities to let them go home for the New Year. For this reason, she was criminally detained by the authorities in March 2011 on suspicion of "picking quarrels and provoking trouble." The case was heard by the Beijing, Chaoyang District People's Court on August 12; nearly a month later, on September 9, the court issued a guilty verdict and sentenced Wang Lihong to nine months in prison. The film documents her case, and raises questions about the accountability of the local government and police. Another one of Ai Xiaoming’s films, “Let the Sunshine Reach the Earth,” documents Wang Lihong’s trial process in more detail.
This film is in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Red Art
This documentary interviews painters, Red Guards, as well as current collectors and researchers in China and the United Kingdom. It presents the emergence, spread, and impact of the propaganda posters during the Cultural Revolution. The film includes interviews with Liu Chunhua, the author of Chairman Mao Goes to Anyuan, Guangzhou painter Li Xingtao, Guangzhou old Red Guard Zhou Jineng, and others. Art museum personnels, art critics, journalists, professors, and researchers in both China and the United Kingdom speak about their understanding of the art of the Cultural Revolution from various perspectives.
This film is in Chinese with both English and Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
River of Oblivion
In this film, the filmmaker accompanied volunteer Xie Yihui as she visited the parents of students who died in the 2008 Sichuan earthquake to find people with knowledge of the architectural blueprint of the Beichuan Middle School. This documentary presents the rise of earthquake tourism and records the mindset of volunteers, bereaved parents, and tourists at the anniversary of the earthquake. This film is interspersed with historical film materials of Beichuan Middle School’s building samples taken by parents in 2008, as well as architect Zhu Tao’s analysis of the construction drawings and building quality. It also shows the perceptions of mothers, teachers, and photographers.
This series of films are in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Songs of Maidichong Village, The
This film was shot in a village called Maidichong in the mountains of Yunnan Province. The village is inhabited by a community of Miao people who are Christians. 100 years ago, the British missionary, Mr. Burghley, came to this village, fostered the Miao language, and brought faith, education, and medical care to the Miao people. This movie tells this history and how their journey of faith was brutally suppressed during the Cultural Revolution. It also presents the challenges they face today.
Film and Video
Spark
<i>Spark</i> tells the story of a group of young intellectuals who risked their lives to voice their opinions about the Chinese Communist Party in the 1950s and 1960s. Following the Hundred Flowers Campaign of 1957, many intellectuals were branded as Rightists and banished to work and live in rural China. A group of students from Lanzhou University were among those sent to the countryside. There, they witnessed mass famine which resulted from government policies to collectivize agriculture and force industrialization in rural China. Shocked and angered by the government’s lack of response to the Great Famine, these students banded together to publish <i>Spark</i>, an underground magazine that sought to alert the Chinese population of the unfolding famine. The first issue, printed in 1960, included poems and articles analyzing the root causes of failed policies. However, as the first issue of <i>Spark</i> was mailed and the second issue was edited, many of these students, along with locals who supported the team, were arrested. Some of the key members of the publication were sentenced to life imprisonment and later executed, while others spent decades in labor camps.
In this 2014 documentary, Hu Jie uncovers the stories of the people involved in the publication of <i>Spark</i>. He conducts interviews with former members of the magazine who survived persecution, and also shows footage of the manuscripts of the magazine. A digital copy of the original manuscript of the first volume of <i>Spark</i> is also held on our website.
This film was awarded the Special Jury Prize for Chinese Documentary at the 2014 Taiwan International Documentary Film Festival and the Award of Excellence in the Asian Competition. Later, it won the Independent Spirit Award at the Beijing Independent Film Festival.
Film and Video
The Central Plains
Due to poverty in rural areas in Henan Province—part of China’s Central Plains—many farmers contracted AIDS by selling their blood. This documentary dives into the lives of these AIDS patients, depicting the manner in which they cope with life, officials’ responses, and the stories of volunteers who helped the infected villagers. The filmmaker visited several villages with high incidence of AIDS, interviewing and recording people’s accounts of how the “plasma economy” arose. This documentary presents the living condition of families and individuals, especially women and children, who contracted AIDS due to blood donation and blood transfusions, and demonstrates the formation of grassroots organizations.
This film is in Chinese with both Chinese and English subtitles.
Film and Video
The Gulag Book
This movie records how Zhang Xianzhi went from being a soldier to a prisoner and then to an independent writer. His experience and thought process is compared with that of the Russian writer Solzhenitsyn. The title of the film is taken from the title of Zhang Xianzhi's book <i>Anecdotes from the Gulag</i>, which takes the viewer on a journey to China's Gulag Archipelago, a labor camp in Sichuan. The extreme conditions and little-known tragic history of the camp are presented. The movie is 42 minutes long and was filmed in 2012.
Film and Video
The Train to My Hometown
As the Lunar New Year approached in 2008, the main north-to-south railway line, the Beijing-Guangzhou line, was halted and the trains stopped running due to tickets being overbooked. With the trains still not running, thousands of migrant workers from Guangdong gathered at the Guangzhou Railway Station, waiting for trains bound for their hometowns. The Guangdong Province government immediately launched an emergency transportation plan. For the first time, the trading center hall where the Canton Fair was held was transformed into a waiting room for migrant workers. Many volunteers provided services to relieve the fears of worried migrant workers.
The crowd began to panic as rumors swirled, and people were trampled underfoot. One was a young female worker, Li Hongxia. Another migrant, Li Manjun, who was eager to travel home to get married, was electrocuted and died after attempting to jump onto the train. This documentary records the chaos at the Guangzhou Railway Station during the Lunar New Year’s Eve period, from January 27 to February 6, 2008. The filmmaker also visited Shenzhen, Shaoguan, Ruyuan, as well as conducted interviews in victims’ hometowns in Jianli, Hubei, and the rural regions of Yueyang, Hunan.
This film is in Chinese with both English and Chinese subtitles.
Film and Video
Though I Am Gone
On August 5, 1966, Bian Zhongyun, a 50-year-old vice principal of the Girls High School affiliated with Beijing Normal University, was beaten to death. The murder was by some of her students, a group of female Red Guards from the school. Bian was the first educator to be killed in Beijing during the Cultural Revolution. The night Bian was killed, Deng Xiaoping's two daughters, Deng Nan and Deng Rong, found Bian's husband and told him that they could only say that Bian died of high blood pressure due to illness, but not that Bian was killed. In the end, no one was criminally prosecuted.
This film is widely regarded as one of Hu Jie's most famous for its portrayal of Bian's husband, Wang Jingyao, and his efforts to document his wife's murder.
Follow director Hu Jie on his <a href="https://www.youtube.com/@jiehu6613">YouTube channel</a>.
Film and Video
Why Are Flowers So Red
This film follows the stories of environmental activist Tan Zuoren and artist Ai Weiwei. In July 2009, Tan Zuoren was charged with the crime of “Inciting subversion of state power,” and his trial was held in Chengdu, Sichuan Province. Ai Weiwei was invited by Tan’s lawyer to testify in court, but the night before the trial, he was assaulted by the police and detained in a hotel. To everyone’s surprise, Ai turned on the tape recorder before the police entered his residence and managed to record the incident. Later, Ai and his colleagues released a documentary about this incident, titled “Disturbing the Peace” (or “Laoma Tihua”).
This film interviews the people behind the scenes of “Disturbing the Peace,” including the director, photographers, editors, and audiences of the film, who discuss the relationship between citizens and government authority.
This series of films are in Chinese with Chinese subtitles.