
Songs of Maidichong Village, The
This film was shot in a village called Maidichong in the mountains of Yunnan Province. The village is inhabited by a community of Miao people who are Christians. 100 years ago, the British missionary, Mr. Burghley, came to this village, fostered the Miao language, and brought faith, education, and medical care to the Miao people. This movie tells this history and how their journey of faith was brutally suppressed during the Cultural Revolution. It also presents the challenges they face today.

Pastor Wang Yi's Anthology: Carrying the Cross - A History of Chinese Family Churches
Wang Yi, of Chengdu, Sichuan Province, is a well-known Chinese intellectual who later became a pastor. The Early Rain Reformed Church that he led was one of the most famous unregistered churches in China. The church occupied the floor of an office building in Chengdu and had its own bookstore, seminary, and pre-school. It regularly had services of hundreds of people. Later, the church had internal conflicts, while at the same time Wang became more outspoken in his criticism of the government. In 2018, he criticized Xi Jinping for abolishing term limits and allowing himself to become ruler of China for life. Pastor Wang was sentenced to nine years in prison in 2019.
This book is based on the recordings of Pastor Wang's classes at Early Rain in 2018. The first five chapters were reviewed by Pastor Wang himself, but he was arrested before he could complete the review of the last five chapters. The essays cover key issues that concerned Wang, including the role of the church in China as a city on the hill, the role of the Reform church in China, and the history of unregistered churches in China.

Killing and Hijacking: Tibet's Cultural Revolution Through the Lens
In 1966, when the flames of the Cultural Revolution began to spread, writer Tsering Woeser (唯色) was born in the General Hospital of the Tibetan Military Region. Her father was an officer in the People's Liberation Army (PLA) in Tibet at the time, and an avid photographer. Through his camera lens, the officer recorded the most comprehensive collection of images of the Cultural Revolution in Tibet to date. Tsering Woeser, on the other hand, restores and records the story behind the camera lens: It was an attempt to fight against oppression and preserve the true history of Tibet during the Cultural Revolution.

Gu Zhun and His Times
This book is about Gu Zhun, a Chinese economist, historian and philosopher. Gu Zhun was the first person to put forward the theory of China's socialist market economy, which became a key concept in the Reform era, helping to justify the use of markets in a socialist system. He also devoted himself to the study of politics, history and philosophy, translating several foreign classic works on economics and democracy and writing a large number of articles. Due to his independent thinking and dissent, he suffered repeated political persecution, including during the Anti-Rightist Campaign and the Cultural Revolution (for more information on Gu Zhun, see his biographical entry). As he personally experienced the Anti-Rightist Campaign, the Great Famine, and the Cultural Revolution, his diary is also considered a valuable source of information on these historical events. By documenting and analyzing his life, thoughts, and the eras in which he lived, Wang's book shows how Gu Zhun persisted in his "pursuit and search for the freedom and equal rights that are inherent to all human beings " (author's preface) in an era when independent thinking was suppressed. This book was published in 2015 by the Great Mountain Culture Publishing House in Hong Kong.

When the Iron Bird Flies: China's Secret War in Tibet
Around the eighth century A.D., the founder of Tibetan Buddhism, Guru Rinpoche, prophesied, "When the iron bird flies in the sky and the iron horse runs on the earth, the Tibetans will be dispersed all over the world like ants, and the Buddha's Dharma will be spread into the land of the red people." More than 1,000 years later, in the middle of the 20th century, the Chinese Communist Party drove the "iron bird" across the sky and rode the "iron horse" across the plateau. The Tibetans courageously rose up to resist resulting in with countless deaths countless deaths. Those who survived were forced to leave their homeland and live in exile in India, drifting around the world. Thus, the prophecy came true. From a military point of view, the Tibetan war in Tibet was a victory, but it received only minimal publicity. The official version of the Party's history is either vague or evasive about the bloody massacre during the entry into Tibet, attempting to cover it up by "suppressing armed rebellion" and "purging counter-revolutionaries". More than sixty years later, this war has yet to be demystified. Li Jianglin, an independent scholar, was moved by the tragedy of the war and the plight of the Tibetans, and endeavored to restore the historical facts. Since 2004, she has devoted herself to research, visiting hundreds of Tibetan elders, searching for tens of thousands of historical materials, collecting military archives, and comparing them with the official published materials of the Communist Party of China, in order to present memories of past, little by little.

Sky Burial: The Fate of Tibet
In this book, author Wang Lixiong presents his arguments with a great deal of personal experience and field work. The book covers the history of the Tibetan issue, the current situation, and various aspects. The book was first published by Mirror Books in Hong Kong in 1998, and an updated edition was released in 2009.

Tibet in Agony: Lhasa 1959
Traveling Chinese history scholar Li Jianglin began working on the Tibet issue in 2004. She has traveled to India every year in search of Tibetan refugees, visited 14 Tibetan refugee settlements in India and Nepal, contacted more than 200 exiled Tibetans from the three regions of Tibet, and personally interviewed the Dalai Lama in Dharamsala, the seat of the Tibetan government-in-exile, in 2008. In 2010, Li Jianglin completed her book <i>Lhasa 1959!</i> by drawing on interviews, information searches, and rare historical photographs provided by the Tibetan government in exile, in the hope of reconstructing the little-known history of the Dalai Lama's departure from Tibet in 1959. The book was published by Taiwan's Lianjing Publishing House in 2010 and reprinted in 2016.
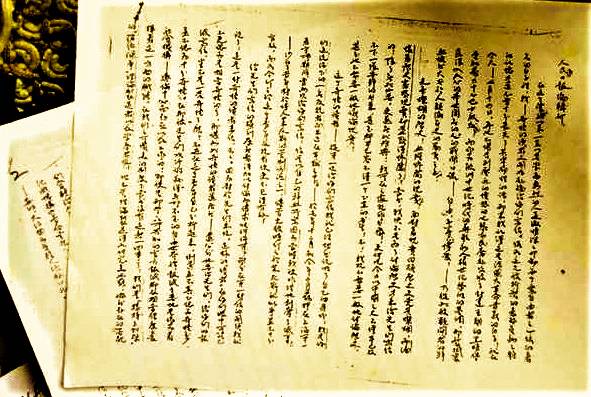
Lin Zhao: A Letter to the Editorial Board of People's Daily
This is one of the most significant essays written by Lin Zhao, the pen name of the Christian intellectual Peng Lingzhao, who was born on January 23, 1932 in Suzhou.
In 1947, she attended a Methodist girls school and was baptized. Soon after, however, she joined the underground Communist Party and began writing critiques of the Kuomintang-led government under the pen name Lin Zhao. Before the Communist takeover in 1949, Lin Zhao ran away from home to attend a journalism school run by the party. During this time she joined party campaigns to eradicate the landholding gentry that ran local society.
Lin Zhao was admitted to the Chinese Department of Peking University in 1954. It was there that she broke with Communism and gradually rediscovered her Christian faith. She was classified as a rightist in 1957 for speaking up for other students. During this time, she met Zhang Chunyuan, one of the founders of the magazine "Spark," which the China Unofficial Archives also holds. She contributed two epic poems to the magazine. The magazine was shut down in 1960 and people affiliated with it were detained, including Lin.
She was released on medical parole in early 1962 due to tuberculosis, but was arrested and imprisoned again in December of the same year. She was detained in Shanghai No. 1 Detention Center and Tilanqiao Prison. When she was denied a pen and paper, she sometimes used a sharpened straw or chopstick to prick her finger and write in blood.
While in prison, she wrote a large number of texts, including the 140,000-word essay to <i>People’s Daily</i> that we feature here. This essay is the fullest expression of Lin’s political beliefs. She wrote it in 1965, dating it July 14 because it was the date of the storming of the Bastille in the French Revolution. It took Lin five months to finish the letter, which ran to 137 pages. She wrote the essay in ink, but stamped it repeatedly with a seal bearing the character “zhao” that she inked in her own blood.
The letter has not (yet) been translated into English so a few salient points are worth mentioning.
As Lin’s biographer, the Duke University professor Lian Xi wrote in his biography of Lin (<i>Blood Letters: The Untold Story of Lin Zhao, a Martyr in Mao’s China</i>, Basic Books, 2018):
“Lin Zhao challenged the theory of a continuous ‘class struggle,’ which the Communists saw as intrinsic to human history and from which there was no escape. Since the 1920s, the CCP had looked upon this theory as an immutable truth and had used it to justify the so-called dictatorship of the proletariat after 1949….”
Lin Zhao scoffed at this. ‘I do not ever believe that, in such a vast living space that God has prepared for us, there is any need for humanity to engage in a life-and-death struggle!’ The CCP dictatorship was but a modern form of ‘tyranny and slavery,’ she wrote in her letter to the party’s propagandists.
“'As long as there are people who are still enslaved, not only are the enslaved not free, those who enslave others are likewise not free!,' she wrote. Those seeking to end Communist rule in China must likewise not ‘debase the goal of our struggle into a desire to become a different kind of slave owner.' ‘The lofty overall goal of our battle dictates that we cannot simply set our eyes on political power—the goal must not and cannot be a simple transfer of political power!’"
“The end was ‘political democratization… to make sure that there will never be another emperor in China!"
Professor Lian continues: “Lin Zhao wrestled with the moral question of whether violence was a justified means to that end. Her Christian faith had hardened her for the fight. At the same time, it also tempered her opposition. She acknowledged the occasional ‘sparks of humanity’ even in those who were at the ‘most savage center’ of Chinese communism. As strenuously as she argued against her imprisonment, against Mao’s dictatorship, and for a free society, she was unable to sanction violence in that struggle. ‘As a Christian, one devoted to freedom and fighting under the Cross, I believe that killing Communists is not the best way to oppose or eliminate communism.’ She admitted that, had she not ‘embraced a bit of Christ’s spirit,’ she would have had every reason to pledge ‘bloody revenge against the Chinese Communist Party.’”
The same year that the letter was finished, Lin Zhao was sentenced to 20 years for counterrevolutionary crimes. On April 29, 1968, the sentence was changed to death and she was executed on the same day. She was 36 years old.
