
Gan Cui: The Soul of Peking University-From Lin Zhao to the 1989 Democracy Movement
This book was originally published in the series *Micro Traces of the Past* - Documentary Volume - No. 6, edited by Huang Heqing, founded in 2007. Gan Cui, a student at Renmin University of China, was classified as a rightist in 1957. He became lovers with Lin Zhao, a rightist student who came from Peking University to work in the data room. Gan Cui was later sent to Xinjiang. When he returned, he learned that Lin Zhao had been killed. This book (in 140,000 words) is a manuscript of Gan Cui's memories of Lin Zhao in the context of the 1989 pro-democracy movement.

1966: Memories of Our Generation
This book is a collection of nineteen feature articles by well-known contemporary scholars, researchers, and writers. They recapitulate their own experiences during the Cultural Revolution in a literary style.
When the Cultural Revolution broke out, they were all young people in their twenties. These reminiscence articles are the result of a rare collective reflection after the end of the Cultural Revolution. The authors described their own experiences during the Cultural Revolution in the articles, providing a personal perspective on history.
The chief editor of this book is the philosopher and activist Xu Youyu, a former researcher at the Institute of Philosophy, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Xu signed and made suggestions on Charter 08, and also is a co-founder of the New Citizens Movement. Since 2015 he has resided in New York City, where he has been a visiting scholar at the New School for Social Research.
This book was published by China Federation of Literary and Art Circles Publishing Corporation in 1998.

The Collected Works of He Jiadong
He Jiadong is a Chinese publisher. He joined the Chinese Communist Party at an early age. After 1949, he founded the Workers' Publishing House, one of the propaganda mouthpieces of the CCP. In 1957, he was designated as a rightist and later labeled as an anti-Party element. In 1965, Kang Sheng criticized him. He was sent down to Chengwu County in Shandong Province, where he was put under local control for 14 years. During the Cultural Revolution, he was taken back to Beijing and criticized, which affected his family and led to the unnatural death of his mother and two sons. In 1979, after the rightist was corrected and completely rehabilitated, he became the executive vice-president and deputy editor-in-chief of the Workers' Publishing House; in 1983, he founded the monthly <i>Rensheng (Life)</i>. In 1984, he founded <i>Kaituo (Pioneering)</i> magazine. He was investigated for publishing Liu Binyan's <i>The Second Kind of Loyalty</i>, and resigned from his post in 1985. The above weekly newspapers, bimonthly magazines and websites were all suspended and closed by the authorities. He has written a large number of articles exploring China's development path from the end of authoritarianism to constitutional democracy. He himself had a 60-year career as a "red publisher" but never had the freedom to publish. Even his own collection of essays was never published. Until the end of his life, he never saw a printed volume of his essays—the printed books were seized and confiscated by the Chinese authorities.
The book can be purchased <a href="https://www.fellowspress.com/shop1/p/-4"> link</a>.

First Man against the Cultural Revolution and His Co-Conspirators, The
On August 8, 1966, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China adopted the "Sixteen Articles" of the Cultural Revolution. Soon after, Liu Wenhui, a young mechanic in Shanghai who had been labeled as a "rightist" in 1957, wrote pamphlets and leaflets clearly opposing the Cultural Revolution, the "Sixteen Articles", and authoritarianism and tyranny. He was arrested on November 26 of that year. Four months later, he was executed for "counter-revolutionary crimes." Liu Wenhui became the first person known to have been publicly shot for opposing the Cultural Revolution. The author of this book, Liu Wenzhong, was Liu Wenhui's co-defendant and survived thirteen years in prison. In this book, Liu Wenzhong describes in detail his brother Liu Wenhui's ideology as well as how he was killed by the tyrannical government.

Blood Letters: The Untold Story of Lin Zhao, A Martyr in Mao's China
This book is the brainchild of Prof. Lian Xi of Duke University, U.S.A. In March 2018, it was published in English by Basic Books in the U.S.A. In 2021, it was published in Chinese by Taiwan Business Press. Based on a large amount of historical materials as well as first-hand interviews, this book reconstructs Lin Zhao's life. It depicts the political development before and after the birth of New China, and presents the resilient will and beliefs of intellectuals in this era.
To purchase this book, please visit [the publisher](https://www.hachettebookgroup.com/titles/lian-xi/blood-letters/9781541644229/?lens=basic-books), or a bookseller.

Yangmou - The Beginning and End of the Anti-Rightist Movement
The revised edition of this book was published by *Open Magazine* in Hong Kong in 2007. The first edition was published in 1991 and was revised and reprinted twice, in 1993 and 1995. The book collects a large amount of information about the anti-rightist movement, including survey interviews with victims of the anti-rightist movement and their relatives and friends. It is a complete record of the anti-rightist movement, which comprehensively analyzes and discusses the whole process of the anti-rightist movement, as well as its ins and outs, causes and consequences. Regarding the number of "rightists," the statistics of the CCP authorities had been limited to 550,000 people. According to Ding Lyric's analysis, there were about 1.2 million people who were labeled as "rightists" in the Anti-Rightist Movement.

China's "Left Scourge"
The author of this book, Lu Jianhua (pen name Wen Lu), was a former member of the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences who published this book in 1993. He was sentenced to 20 years in prison in 2005 for "allegedly leaking state secrets" in connection with the "espionage case" involving journalist Cheng Xiang.

A Non-governmental White Paper on the June Fourth Massacre
At the turn of the spring and summer of 1989, democratic protests broke out in Beijing and other cities in China. In the early hours of June 4, the Chinese government dispatched troops to suppress the movement. In 2009, on the occasion of the 20th anniversary of the June 4th Incident in 2009, some participants in the movement jointly released the "Unofficial White Paper on the June 4th Incident". The book has 48 pages and a large number of illustrations.
This white paper attempts to provide a complete political background and legal analysis of the events based on reports from Chinese newspapers, radio and television stations at the time, as well as memoirs and interviews that have been published over the past 20 years. Participants in this book believe that the Chinese government has not conducted a comprehensive investigation and objective evaluation of the June 4th Incident, and has long blocked relevant information and prohibited private investigation and discussion of the matter. The report is called a "white paper" to emphasize its rigor and normative nature.
Participants in this book include Hu Ping, Yan Jiaqi, Wang Juntao, Wang Dan, Yang Jianli and others. The book was written by Li Jinjin, a doctor of law.

Lin Zhao: No Longer Forgotten
This book contains a number of articles in memory of Lin Zhao. It concerns the death of Lin Zhao as well as Lin Zhao's love, pursuits, and disillusionment. This book was published by Changjiang Literature and Art Publishing House in 2000.

Liushahe Essay
Liushahe is a famous Chinese writer and scholar, who entered Sichuan University in the fall of 1949, and was criticized and stigmatized nationwide during the 1957 Anti-Rightist Movement for his work *Grass and Trees* named by Mao Zedong himself, and then subjected to a variety of labor reforms (building roads during the day and sawing wood in the evening) for a cumulative total of 20 years. In 1979, he was transferred back to the Sichuan Provincial Literature Federation. Since 1985 he has been writing full-time, and has published a number of books, including *Essays on the Liusha River*. This book was published by Sichuan Literature and Art Publishing House in 1995. Many of the essays are related to his experiences when he was under labor reform. In November 2019, Liushahe passed away in Chengdu at the age of 88 due to illness.
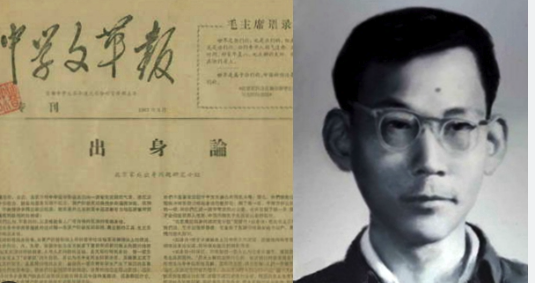
On Family Background
Yu Luoke (May 1, 1942 - March 5, 1970): Worker, freelance writer, and public intellectual.
Yu was born into an educated family in northeastern China, which for a period of time was under Japanese occupation. His father studied on a state scholarship in Waseda University in Tokyo, while his mother came from a wealthy family in Beijing and studied business at Tokyo Girls High School. When the two returned to China, they went into business, married, and had three children.
When the CCP took power, the family was declared part of the “bourgeois class” and like other “black elements”--classes of people who the party declared to be enemies–was persecuted. The father was arrested in 1952 on charges of tax evasion and released. In 1957, Yu Luoke’s parents were declared Rightists and sent to labor camps. In 1959, Yu graduated from high school with highest honors but as the offspring of an undesirable class was not permitted to attend university. In 1961, he was allowed to work on a farm in a Beijing suburb, where he realized that class identity was also important in rural China–landlords and their children were even beaten to death. In 1964 he returned to the city and apprenticed at a machinery factory. Yu realized that he was part of an untouchable caste in Maoist China and would be condemned forever, no matter what he believed or how hard he worked.
These experiences were the genesis of Yu’s essay, which became one of the most famous texts of the Mao era. Yu wrote it at the start of the Cultural Revolution. The ten-thousand character essay is called chushenglun, or “On Family Background” (sometimes translated as “On Class Origins"). In it, he warned that the “five black categories'' were becoming a permanent underclass, while China’s rulers were from the hongwulei, or “five red categories:” poor and lower-middle peasants, workers, revolutionary soldiers, revolutionary officials, and revolutionary martyrs, including their family members, children, and grandchildren. He warned of a new ruling class based on bloodlines.
The essay was published in a journal that Yu and his brother Yu Luowen called the "Journal of Secondary School Cultural Revolution." In January 1967, about thirty thousand copies were printed, and the young men began distributing them around the capital, selling them for two cents a copy. They sold out in a few hours. In February, they printed another eighty thousand copies.
Soon, hundreds of letters each day arrived at Yu Luoke’s local post office—so many that he had to go collect them in person. The missives detailed how the Communists’ policies had caused them to suffer. People traveled from across China to visit them at their home, excited that someone finally had uncovered how the Chinese Communist Party ruled. The editorial board was expanded to twenty people, and the group sponsored debates and seminars.
The Journal was closed down in April 1967. Yu Luoke began to write on economic inequality. In January 1968, he was arrested. Two years later, on 5 March 1970, Yu was executed by firing squad at Beijing Workers Stadium.
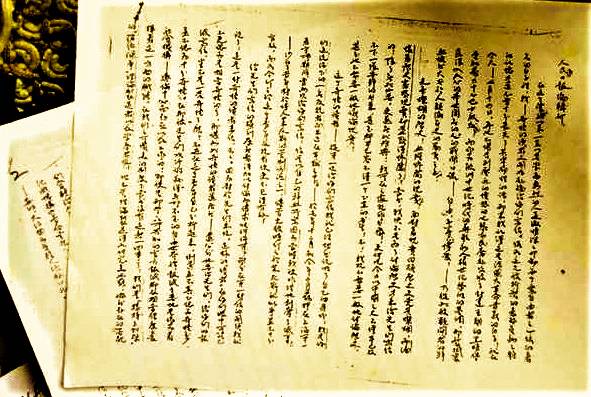
Lin Zhao: A Letter to the Editorial Board of People's Daily
This is one of the most significant essays written by Lin Zhao, the pen name of the Christian intellectual Peng Lingzhao, who was born on January 23, 1932 in Suzhou.
In 1947, she attended a Methodist girls school and was baptized. Soon after, however, she joined the underground Communist Party and began writing critiques of the Kuomintang-led government under the pen name Lin Zhao. Before the Communist takeover in 1949, Lin Zhao ran away from home to attend a journalism school run by the party. During this time she joined party campaigns to eradicate the landholding gentry that ran local society.
Lin Zhao was admitted to the Chinese Department of Peking University in 1954. It was there that she broke with Communism and gradually rediscovered her Christian faith. She was classified as a rightist in 1957 for speaking up for other students. During this time, she met Zhang Chunyuan, one of the founders of the magazine "Spark," which the China Unofficial Archives also holds. She contributed two epic poems to the magazine. The magazine was shut down in 1960 and people affiliated with it were detained, including Lin.
She was released on medical parole in early 1962 due to tuberculosis, but was arrested and imprisoned again in December of the same year. She was detained in Shanghai No. 1 Detention Center and Tilanqiao Prison. When she was denied a pen and paper, she sometimes used a sharpened straw or chopstick to prick her finger and write in blood.
While in prison, she wrote a large number of texts, including the 140,000-word essay to <i>People’s Daily</i> that we feature here. This essay is the fullest expression of Lin’s political beliefs. She wrote it in 1965, dating it July 14 because it was the date of the storming of the Bastille in the French Revolution. It took Lin five months to finish the letter, which ran to 137 pages. She wrote the essay in ink, but stamped it repeatedly with a seal bearing the character “zhao” that she inked in her own blood.
The letter has not (yet) been translated into English so a few salient points are worth mentioning.
As Lin’s biographer, the Duke University professor Lian Xi wrote in his biography of Lin (<i>Blood Letters: The Untold Story of Lin Zhao, a Martyr in Mao’s China</i>, Basic Books, 2018):
“Lin Zhao challenged the theory of a continuous ‘class struggle,’ which the Communists saw as intrinsic to human history and from which there was no escape. Since the 1920s, the CCP had looked upon this theory as an immutable truth and had used it to justify the so-called dictatorship of the proletariat after 1949….”
Lin Zhao scoffed at this. ‘I do not ever believe that, in such a vast living space that God has prepared for us, there is any need for humanity to engage in a life-and-death struggle!’ The CCP dictatorship was but a modern form of ‘tyranny and slavery,’ she wrote in her letter to the party’s propagandists.
“'As long as there are people who are still enslaved, not only are the enslaved not free, those who enslave others are likewise not free!,' she wrote. Those seeking to end Communist rule in China must likewise not ‘debase the goal of our struggle into a desire to become a different kind of slave owner.' ‘The lofty overall goal of our battle dictates that we cannot simply set our eyes on political power—the goal must not and cannot be a simple transfer of political power!’"
“The end was ‘political democratization… to make sure that there will never be another emperor in China!"
Professor Lian continues: “Lin Zhao wrestled with the moral question of whether violence was a justified means to that end. Her Christian faith had hardened her for the fight. At the same time, it also tempered her opposition. She acknowledged the occasional ‘sparks of humanity’ even in those who were at the ‘most savage center’ of Chinese communism. As strenuously as she argued against her imprisonment, against Mao’s dictatorship, and for a free society, she was unable to sanction violence in that struggle. ‘As a Christian, one devoted to freedom and fighting under the Cross, I believe that killing Communists is not the best way to oppose or eliminate communism.’ She admitted that, had she not ‘embraced a bit of Christ’s spirit,’ she would have had every reason to pledge ‘bloody revenge against the Chinese Communist Party.’”
The same year that the letter was finished, Lin Zhao was sentenced to 20 years for counterrevolutionary crimes. On April 29, 1968, the sentence was changed to death and she was executed on the same day. She was 36 years old.

Li Yizhe Incident - A Bottom-Up Appeal for Democracy and the Rule of Law in the Cultural Revolution
Li Yizhe is the signature of a famous large-print newspaper, “About Socialist Democracy and the Rule of Law,” during the Cultural Revolution in mainland China. The newspaper was co-authored by three people: Li Zhengtian, a student at the Guangzhou Academy of Fine Arts; Chen Yiyang, a high school student; and Wang Xizhe, a factory worker. The name Li Yizhe was created with characters taken from each of the three names.
"Li Yizhe" wrote three drafts from September 13, 1973 to November 7, 1974. On November 10, 1974, the newspaper was publicly posted on the streets of Guangzhou, with a total of sixty-seven sheets of white paper and more than 26,000 words. The content called for socialist democracy and the rule of law, in the form of a critique of the "Lin Biao system." It pointed directly at the shortcomings of the CCP's ultra-leftist movement that had trampled on democracy and the rule of law since the founding of the CCP. The newspaper pointed out that the social and historical conditions under which Lin Biao's group emerged reflected the ideology of China's feudal society, which had lasted for more than 2,000 years, and that the essence of Lin Biao's counter-revolutionary group reflected the ideology of the extreme left. Without naming names, the broadsheet also pointed out the many crimes of those in power and, in connection with these phenomena, analyzed the serious problems of the socialist "system" itself. Li Yizhe and others were arrested in 1977 and rehabilitated a year later.

Lin Zhao Anthology
The Lin Zhao Anthology contains nearly one hundred of Lin Zhao's works, including essays, poems, commentaries, and news reports written since her middle school years, as well as all of Lin Zhao's manuscripts and letters that were written in prison and later returned to her family. The collection was edited and compiled by Lin Zhao's friends Tan Chanxue (see separate entry) and Ni Jingxiong, and printed into a book on their own. Most of Lin Zhao’s manuscripts written in her blood in prison were typed on computer by Tan Chanxue. This anthology is the most important historical material used by Prof. Lian Xi of Duke University for his research and writing of the book "Blood Letters: The Untold Story of Lin Zhao, a Martyr in Mao's China."

What Else Did Zhao Ziyang Say - Du Daozheng's Diary
*What Else Did Zhao Ziyang Say - Du zheng's Diary* was published simultaneously in Hong Kong and Taiwan on January 17, 2010 (Hong Kong Tiandi Book Co., Ltd. and Taiwan Printing Literature and Life Magazine Publishing Co). The book is the first to publicize more than 30 unpublished conversations in Zhao Ziyang's recorded oral transcripts, covering a number of major issues. The book is illustrated with a selection of more than 40 rare photographs taken by the author. The book is divided into three parts: upper, middle and lower. It records Zhao Ziyang's exhaustive expressions on topics such as anti-corruption, the nascent bureaucratic capitalist class, federalism, punishment by words, media management, political system reform, and the new leftist trend of thinking.

Yangtze Yangtze
In March 1989, the book Yangtze Yangtze was published by the Guizhou People's Publishing House just as the Tiananmen student protests were about to begin in Beijing. The book fed into this intellectual ferment, challenging the technocratic reasons for the Three Gorges Dam, which eventually would dam the Yangtze River in the name of flood control and electrical power generation.
The book was edited by the journalist Dai Qing, the daughter of a well-known Communist Party activist and leader. The book challenged the project's decision-making process, with a broad array of scientists, journalists, and intellectuals arguing that it was not democratic and did not take into account all viewpoints. It was widely read in China and translated into foreign languages.
After the Tiananmen protests were violently suppressed, Dai Qing was arrested and imprisoned for ten months in Qincheng Prison as an organizer of the uprising. Yangtze Yangtze was criticized as “promoting bourgeois liberalization, opposing the Four Fundamental Principles (of party control), and creating public opinion for turmoil and riots.” The book was taken off the shelves and destroyed, with some copies burned. It became the first banned book resulting from the decision-making process of the Three Gorges Project.
The book is banned in China. The English-language edition can be read online at Probe International: https://journal.probeinternational.org/three-gorges-probe/yangtze-yangtze/.

Liu Xiaobo Memorial Anthology
This book is a collection of essays in memory of the Nobel Peace Prize winner Liu Xiaobo. It was edited by Cai Chu following his death.

When did Chairman Mao decide to lure the snakes out of their holes?
This is an important article in Li Shenzhi's *Collected Writings*, which analyzes in detail why Mao Zedong wanted to "oppose the right," and how he launched the "anti-right" campaign.